In the world of plumbing and construction, the DWV system plays a crucial role. DWV stands for Drain-Waste-Vent, a system designed to remove waste water and sewage from a building and regulate air pressure in the waste-system pipes to aid free flow. This article explores the intricacies of the DWV system and clarifies the differences between common PVC pipes and DWV-rated pipes.
The DWV System Explained
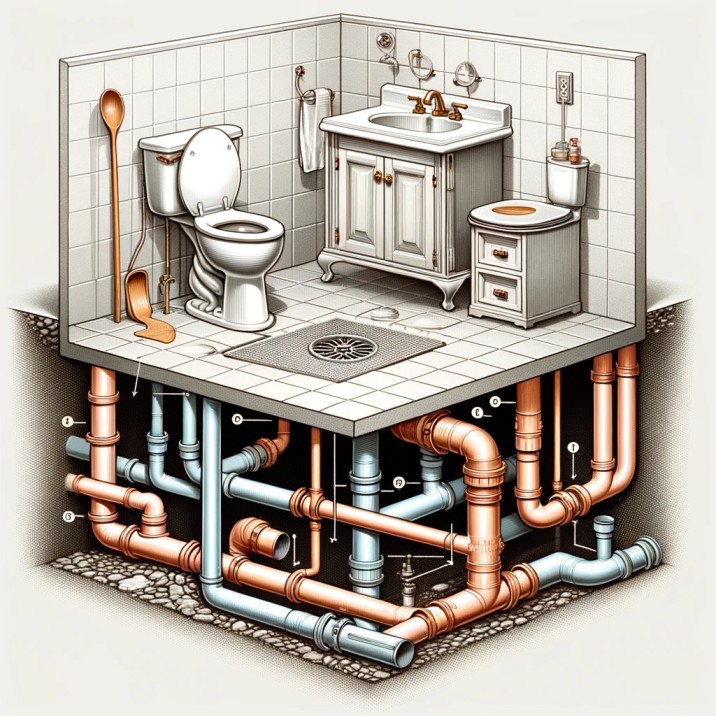
The DWV system is an essential component of residential and commercial buildings. It consists of a network of pipes that carry wastewater and sewage from sinks, toilets, and showers to a sewer or septic system. A key component of this system is the venting pipes, which allow air to enter the plumbing system, ensuring that water flows smoothly and prevents sewage gases from entering the building.
Components of the DWV System
The system includes three main types of pipes:
- Drain Pipes: These pipes remove gray water and waste from appliances and fixtures.
- Waste Pipes: They carry sewage and waste water to a sewer or septic system.
- Vent Pipes: These pipes maintain the balance of air pressure within the plumbing system and release sewage gases outside.
Difference between PVC and DWV Pipes
PVC Pipes
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes are a popular choice in plumbing for their durability, resistance to corrosion, and affordability. They come in different thicknesses and can be used for various applications, including potable water supply, irrigation, and as part of the DWV system.
DWV Pipes
DWV pipes are a subset of PVC pipes specifically designed for drain, waste, and vent applications. The primary difference lies in their ratings and wall thickness. DWV PVC pipes have a thinner wall compared to those used for pressurized water systems, as they do not need to withstand high water pressure. They are also distinguished by different color markings and sometimes a different color.
Key Differences
- Pressure Rating: Regular PVC pipes are designed to handle pressure and are used for water supply lines. In contrast, DWV pipes are not pressure-rated as they only carry wastewater.
- Wall Thickness: DWV pipes have thinner walls as they do not need to withstand the pressure that water supply lines do.
- Diameter and Fittings: DWV PVC pipes often come in larger diameters to accommodate waste and ensure smooth passage without clogs. The fittings for DWV systems, including bends and connections, are also designed to minimize obstruction and facilitate a smooth flow.
Understanding the difference between PVC and DWV pipes is essential for effective plumbing and construction. While both types of pipes may be made from PVC, their specific applications, pressure ratings, and dimensions differ significantly. The proper selection and installation of these pipes ensure the efficient and safe removal of wastewater and the regulation of air pressure in a building’s plumbing system. The DWV system, with its specialized pipes and fittings, plays a crucial role in maintaining sanitary conditions and the overall functionality of any building’s plumbing infrastructure.